Orthopedics and Traumatology - Pathologies
What it is?
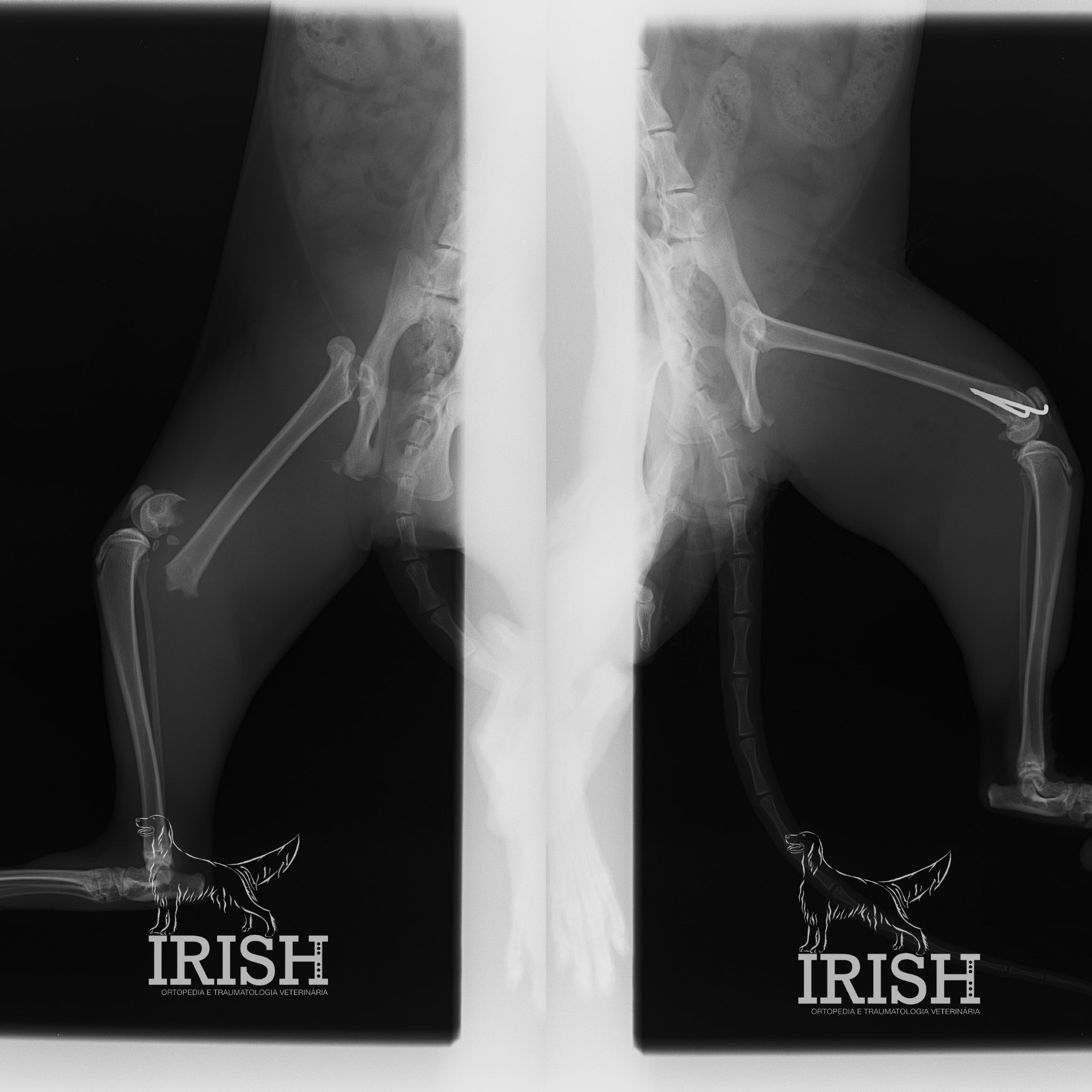
Hip dysplasia is a developmental disease in which the laxity of the hip joint and inadequate acetabular coverage lead to the development of an osteoarthritis process (degenerative disease).
Osteoarthritis will cause bone and joint changes that result in chronic pain and physical restriction for the patient, influencing their quality of life.
How important is screening?
Screening for hip dysplasia, carried out between 5 and 6 months of age, allows preventive measures to be taken to stop the disease from developing. Screening for hip dysplasia consists of carrying out an orthopedic examination and radiographic study in which information is collected that allows the anatomical and clinical conditions of the patient to be studied, thus predicting the possibility of the disease developing.
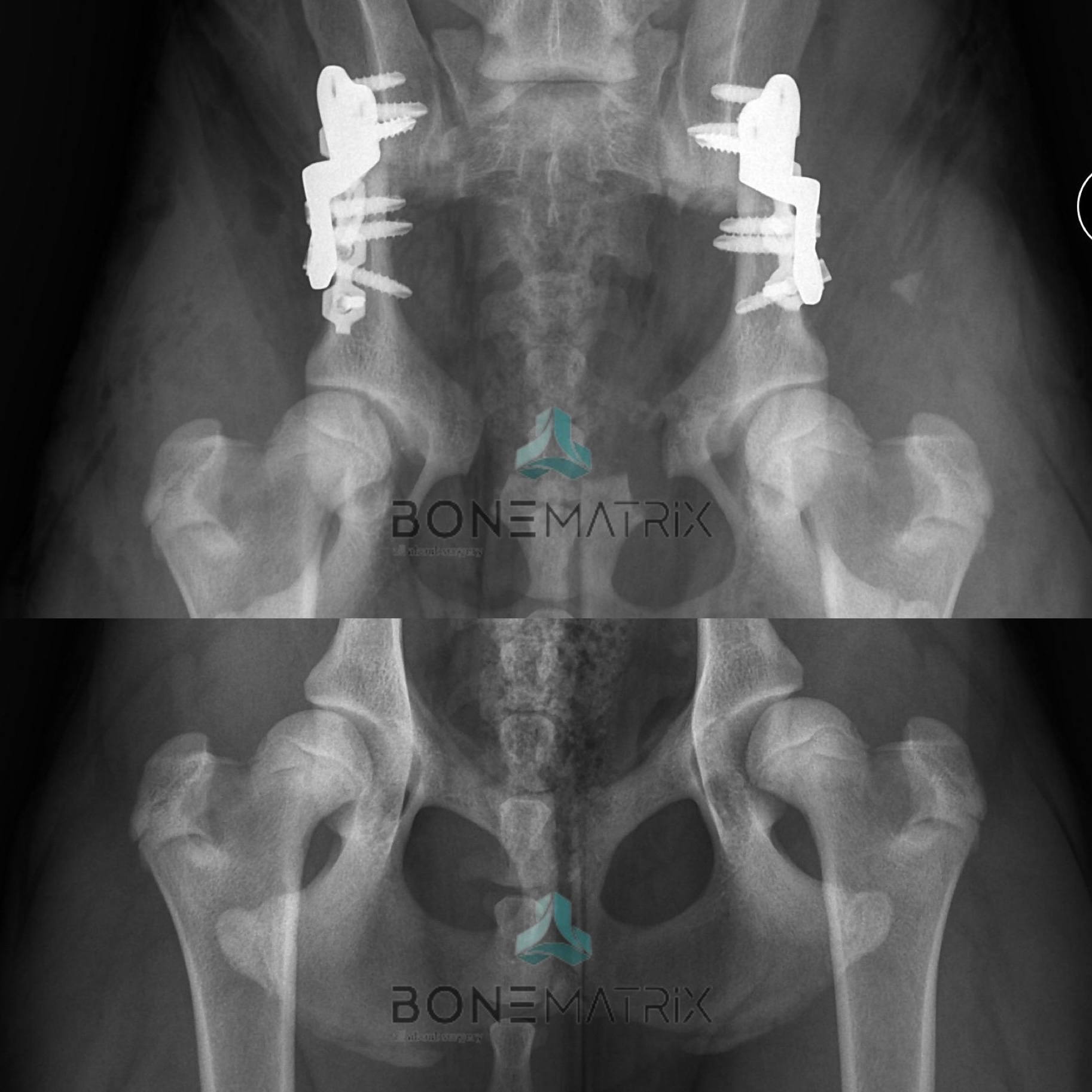
Various surgical options can be considered if a diagnosis is made within this timeframe, including: juvenile pubic symphysiodesis (JPS) and Double pelvic osteotomy (DPO - double pelvic osteotomy). The technique is chosen according to the individual characteristics of each patient.
After this period of growth has passed, similar therapeutic results can only be achieved by performing joint replacement procedures using the Total Hip Replacement (TRH – total hip replacement).
What is the treatment?
The management of hip dysplasia, depending on the degree of conditioning of the disease, can be achieved through drug therapy (in less severe cases), but this does not lead to the treatment of the pathology, but rather to the management of the symptoms, through pain control.
There are various surgical solutions that may be an option, but it is important to stress that early diagnosis is essential if these options are to prevent the disease from developing. Once the growth is complete, a hip prosthesis is the only surgery with similar results in resolving the condition.
What it is?
Elbow dysplasia is a developmental disease based on a lack of congruence between the bones that make up the elbow (humerus, radius and ulna).
Various diseases can arise secondary to the development of this process, such as ununited anconeal process (UAP), fragmented coronoid process (FCP) and osteochondritis dissecans (OCD).
The development of the disease leads to chronic pain and physical conditioning that affect the patient's quality of life.
How important is screening?
Screening for elbow dysplasia, carried out between 5 and 6 months of age, can enable preventive measures to be taken to stop the disease from developing. This screening is carried out by means of an orthopedic examination and a radiographic study.
Various surgical options can be taken in the meantime, including: Distal ulnar osteotomy (DUO – distal ulnar ostectomy), Bi-oblique dynamic proximal ulnar osteotomy (BDPUO – bi-oblique dynamic proximal ulnar osteotomy) e resolução de deformidades angulares responsáveis pela perda de congruência articular. A técnica escolhida é direcionada ao paciente e caso clínico concreto.
Elbow dysplasia in adult animals has surgical options that can also provide satisfactory results, such as proximal abducting ulnar osteotomy (PAUL - proximal abducting ulnar osteotomy) and the sliding humerus osteotomy (Sliding humeral osteotomy).
What is the treatment?
The management of elbow dysplasia, depending on the degree of disease, can be achieved through drug therapy alone or in addition to surgical treatment.
There are various surgical solutions for treating this disease, but ideally they should be performed for preventative purposes, when osteoarthritis changes are not yet present.
What it is?
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease that affects the joints. The main symptoms of this disease are intra-articular pain and restricted movement. Its origin can be varied and it can be caused by a wide range of pathologies, ranging from the immune-mediated, infectious component, to the emergence as a consequence of another primary orthopedic pathology.
How is it diagnosed?
Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed by orthopedic examination, where a loss of joint range of motion, bone and cartilage changes, pain and joint effusion can be identified.
O estudo radiográfico poderá apoiar o diagnóstico revelando alterações ósseas degenerativas na articulação em estudo.
What is the treatment?
Osteoarthritis is a pathology with no cure, but depending on its origin, various techniques can be applied to halt the progression of the disease. When diagnosed early, there are several measures that can be taken so that the presence of the condition does not significantly affect the patient's quality of life.
A escolha da abordagem irá depender da origem do problema, podendo esta variar entre abordagens cirúrgicas (para eliminar o fator de origem do quadro) em associação com terapia medicamentosa (para controlo os sintomas), até ao recurso a terapias adjuvantes que contribuam para a melhoria do ambiente intra-articular.
What it is?
Cranial cruciate ligament rupture is, in most cases, a degenerative disease, but less often it can also be caused by trauma.
A doença degenerativa do ligamento cruzado faz com que este ligamento apresente maior fragilidade em comparação com um ligamento em que a doença não está presente (pela perda progressiva das características normais das fibras que o compõe).
The cranial cruciate ligament is a ligament found inside the knee which contributes to the stability of this joint. This ligament is responsible for preventing cranial movement of the tibia in relation to the femur and internal rotation.
Quando o ligamento rotura perde-se a estabilidade dentro da articulação, sendo este um processo que, para além de inicialmente doloroso, irá resultar no desenvolvimento de um processo de osteoartrite avançada motivado pela inflamação e instabilidade crónica da articulação.
How is it diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the patient's orthopaedic examination, using the drawer or tibial advancement test.
As a complementary diagnostic test, a radiographic study can also be carried out, which shows tibial advancement in relation to the femoral condyles, as well as intra-articular inflammation.
What is the treatment?
There are various surgical procedures aimed at stabilizing the knee in the absence of cranial cruciate ligament integrity. The technique with the best results in stabilizing and preventing/reducing the progression of the osteoarthritis process is the Tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (TPLO – tibial plateau leveling osteotomy).
Vários estudos científicos foram realizados comparando as técnicas empregues com mais frequência nestes casos, sendo estas a imbricação extra-capsular, a TTA (tibial tuberosity advancement) e a TPLO,. Esses estudos concluíram que a técnica de TPLO apresenta resultados significativamente melhores em relação às restantes técnicas estudadas.
What it is?
A rotura de ligamentos é uma patologia frequentemente causada por situações de trauma. Os ligamentos que mais frequentemente são intervencionados são: os ligamentos colaterais, o ligamento redondo e os ligamentos palmares/plantares.
How are they diagnosed?
The integrity of the collateral ligaments is tested by orthopedic examination. X-rays can be used as a complementary means of diagnosis by acquiring stress X-rays, where the joint amplitude is visibly excessive compared to a normal situation.
The round ligament is found in the hip joint. Its rupture is often associated with dislocation of the joint (the femoral head comes out of the acetabulum). This pathology can be identified by physical examination and radiography.
Relativamente aos ligamentos palmares e plantares, no exame ortopédico, a sua lesão poderá ser identificada pela hiperextensão excessiva (plantigradismo) da articulação do tarso ou do carpo. O estudo radiográfico irá evidenciar uma amplitude articular excessiva.
What is the treatment?
The choice of surgical technique to resolve the clinical condition is based on the characteristics of the patient and the affected joint.
In the case of collateral ligaments, it is common to use bone anchors, onde é colocado um ligamento sintético a mimetizar a função do ligamento normal. Este material é fixado ao osso acima e abaixo da articulação por meio de âncoras ósseas.
In the case of the round ligament, the technique of toggle pin where the torn ligament is also replaced with a synthetic ligament that allows the joint to remain stable.
Quando existe lesão dos ligamentos palmares ou plantares, o tratamento, frequentemente, passa pela realização de um procedimento cirúrgico de arthrodesis.
What it is?
Angular limb deformities often have a genetic component, followed by a worsening of the condition during the patient's growth phase. It can also be the result of misaligned bone healing (after a fracture).
As deformidades angulares são responsáveis por: anomalias de marcha no paciente; sobrecarga articular e de ligamentos responsáveis pela estabilização de articulações; e patologias musculares.
A luxação de patela é uma patologia frequentemente diagnosticada que apresenta a sua origem em uma ou várias deformidades angulares. O resultado da existência destas deformidades é, na maioria das vezes, a luxação medial de patela (rótula).
How are they diagnosed?
Angular deformities can be diagnosed by orthopedic examination and radiographic study. The radiographic study is used for pre-surgical planning of the correction.
In cases of medial patellar dislocation, the radiographic study is directed at the femur and tibia bones, showing which deformity is the cause of the problem.
What is the treatment?
There are several surgical options for correcting angular deformities, the technique chosen being based on the patient's characteristics, the deformity present and the location of the deformity.
Entre as técnicas mais utilizadas para a correção de deformidades angulares podemos considerar as osteotomias corretivas de closing wedge (CWO – closing wedge osteotomy) e as osteotomias corretivas de opening wedge (OWO – opening wedge osteotomy).
In cases of patellar dislocation, the correction of this pathology may involve one or more combined techniques: Distal femoral osteotomy (DFO – Distal femoral osteotomy), Proximal tibial osteotomy (PTO – proximal tibial osteotomy), Tibial tuberosity transposition (TTT – tibial tuberosity transposition), sulcoplastia e pateloplastia. Para a correta correção desta patologia é imprescindível a realização de um estudo radiográfico ortogonal dos ossos envolvidos na articulação para perceber qual a deformidade que é responsável pela patologia.
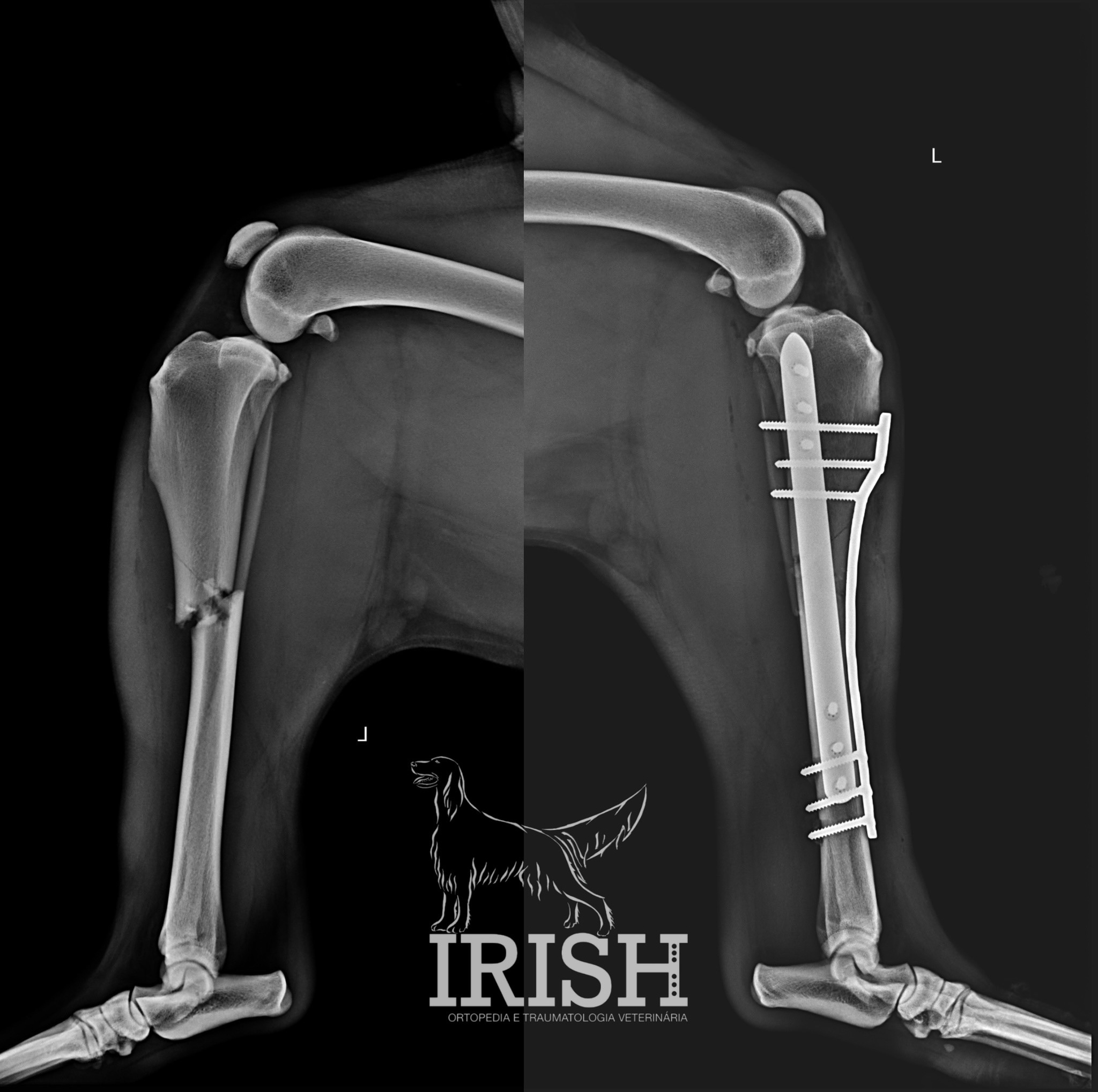
What it is?
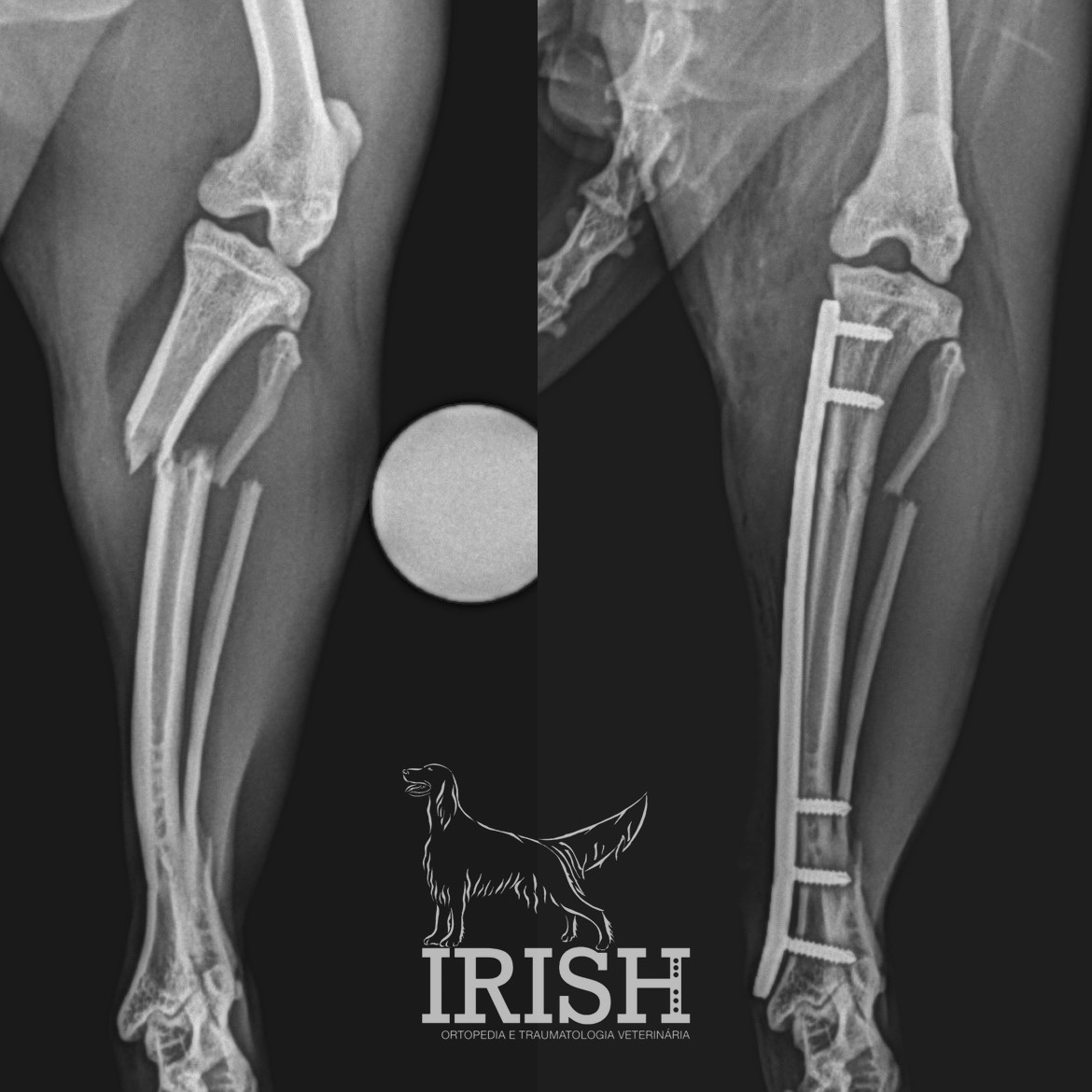
As fraturas surgem na maioria das vezes associadas a situações de trauma. Este trauma poderá ser agudo, a força aplicada ao tecido ósseo excede a sua capacidade elástica e ocorre a fratura, ou então, com menor frequência, poderá resultar de um trauma de baixa intensidade que ocorre de forma frequente (fraturas de esforço).
How are they diagnosed?
As fraturas são diagnosticadas por meio de exame ortopédico. O estudo radiográfico é essencial para diagnóstico e planeamento cirúrgico. Em fraturas articulares, por vezes, é necessário o recurso a um exame complementar de imagem avançada (TAC) para conseguir realizar o diagnóstico, dado o tamanho reduzido dos ossos envolvidos e a existência de sobreposições ósseas na imagem radiográfica.
What is the treatment?
There are various surgical techniques that can be applied in the event of a fracture, the choice of which depends on the characteristics of the fracture and the individual characteristics of the patient.
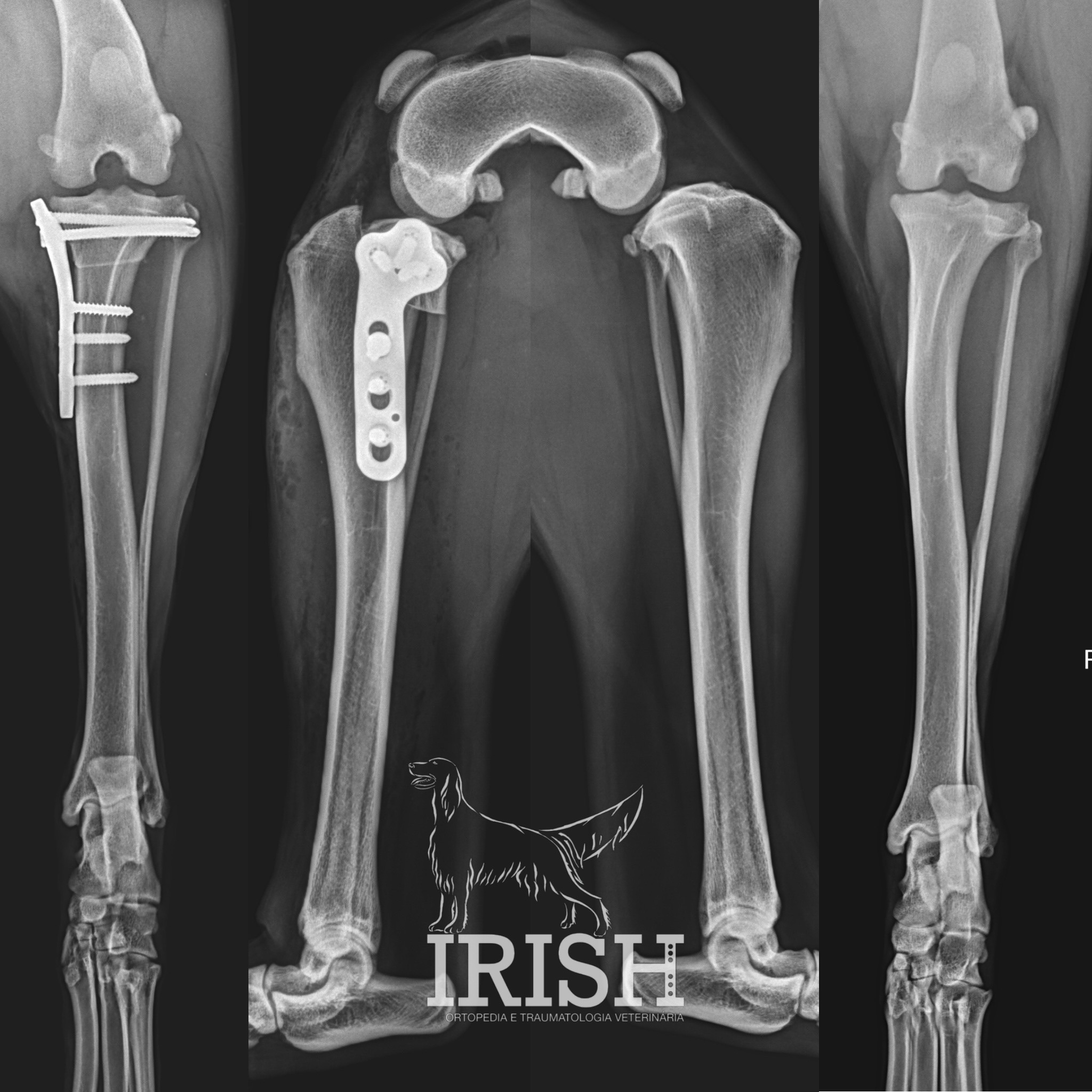
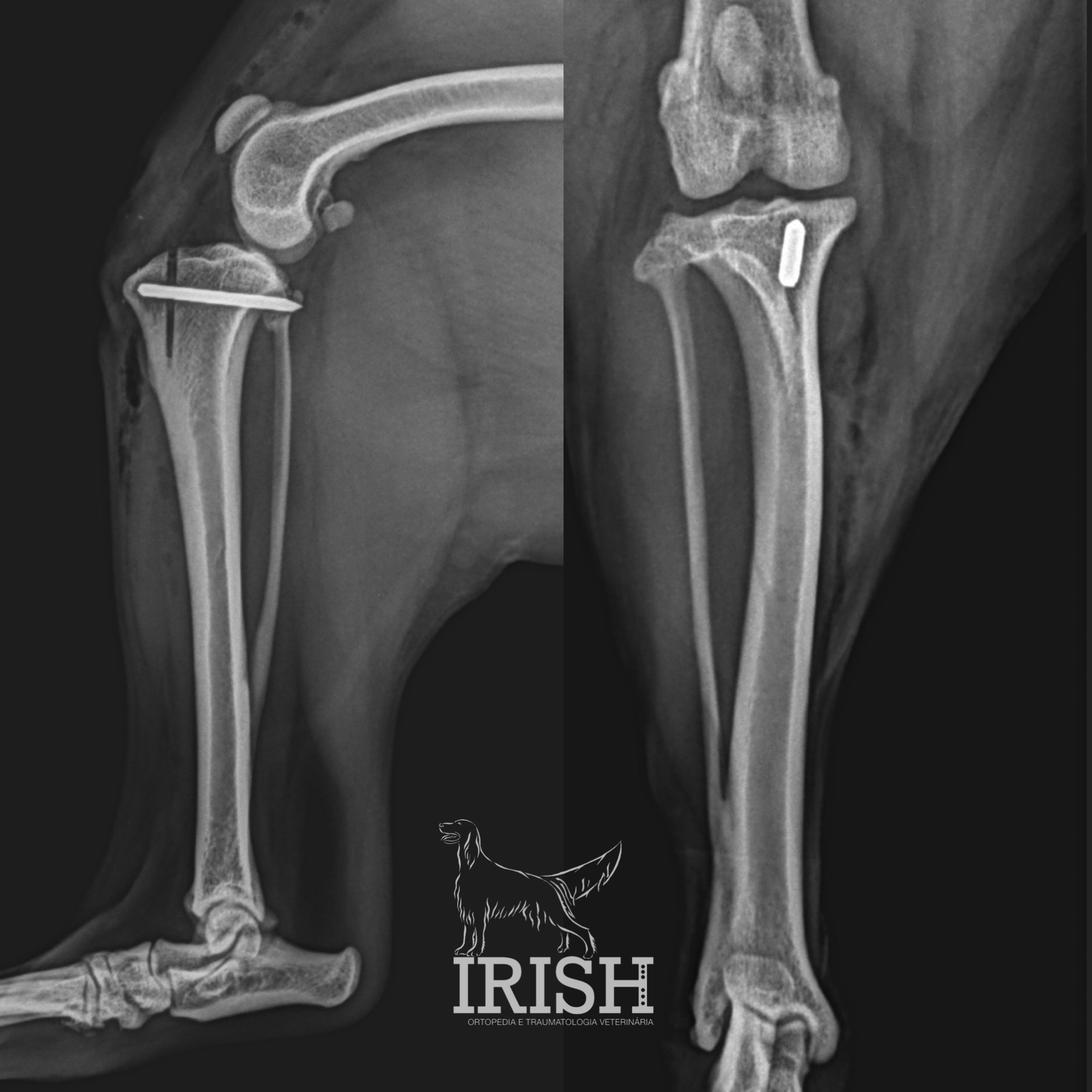
In general, we can use external skeletal fixator (ESF – external skeletal fixator), plates and screws and orthopedics pins..
The correct choice of technique will be essential for the success of the clinical case.
Orthopedics and Traumatology - Surgeries
The surgical technique used must take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the fracture. The choice of surgical procedure will be decisive for a good surgical outcome.
What is it?
External fixators are skeletal fixation devices that use orthopedic pins in association with rods and kneecaps or circular disks. The aim of using this material is to stabilize the bone so that it can heal.
Its configuration and choice of equipment should be considered taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient/bone/pathology.
After bone callus has formed, the equipment is removed from the patient in a simple procedure carried out under sedation.
Common pathologies in which these techniques are recommended: fracture stabilization, corrective osteotomies, joint immobilization.
What is it?
As placas de osteossíntese são materiais utilizados para a estabilização óssea, em associação com parafusos, que as fixam ao osso. As placas de osteossíntese podem assumir várias funções, sendo a sua função escolhida de acordo com as características da fratura/patologia presente. Estes equipamentos categorizam-se em dois grupos principais, as placas DPC e as placas bloqueadas.
These materials are inert and biocompatible and their removal is usually not necessary.
Common pathologies in which these techniques are recommended: fracture stabilization, corrective osteotomies, joint immobilization.
What is it?
Orthopaedic pins are used as a means of stabilization in some fractures with specific characteristics, such as some growth plate fractures or diaphyseal metatarsal/ankle fractures.
Common pathologies in which these techniques are recommended: estabilização de fraturas de placas de crescimento, estabilização de fraturas de metacarpos/tarsos.
What is it?
Os ligamentos sintéticos são materiais inertes e biocompatíveis que têm como objetivo mimetizar a função de um determinado ligamento que por norma se encontra roturado. Esses materiais são normalmente unidos ao osso por intermédio de âncoras ósseas ou toggle pins.
Common pathologies in which these techniques are recommended: joint stabilization.
What is it?
Corrective ostectomies and osteotomies aim to change the anatomical configuration of a bone in order to correct an underlying pathology. Stabilization can be achieved using external fixators or osteosynthesis plates, depending on the individual characteristics of the pathology/patient.
Common pathologies in which these techniques are recommended: elbow or hip dysplasia, cranial cruciate ligament rupture, correction of angular deformities.